Case Studies.
Case #1
Patient presented for evaluation of lower right side. Pt reports having pain to biting and chewing.
Tested teeth #’s 30, 31, 31 tested (+)perc, (+)biting, (-)palp, no response to cold.
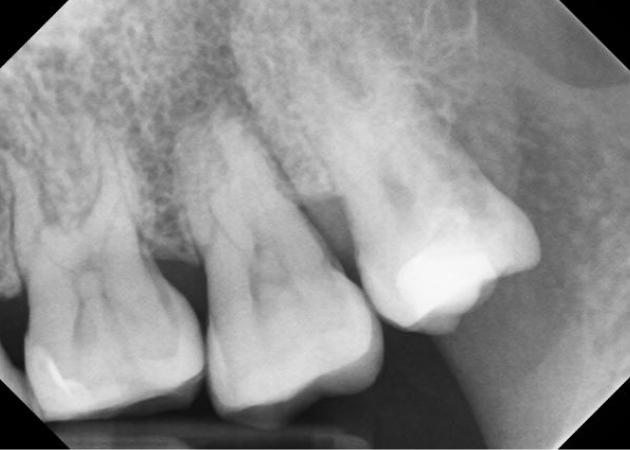
#31
Periradicular dx: symptomatic apical periodontitis
pulpal dx: necrotic
Treatment : Root canal was completed on tooth # 31, anatomy was funky!
Pre Op #31
Post Op #31
Case #2
Patient presented for retreatment of tooth #30
(+)perc, (-)palp, previous RCT
CBCT scan taken, (+)PAP MB root, short fill on mesial and distal roots
#30
Apical: symptomatic AP
Pulpal: previously treated
Retreatment was completed in two visits, patient felt great after first visit.
Retreatment was uneventful.
Pre Op #30
Post Op #30
Case #3
Pt presented for retx # 9. CBCT scan taken, large PAP on 8 and open resorbed apex noted.
# 9 (+)perc, (+)palp, previous RCT, (+)PAP
#09
Periradicular Dx: symptomatic apical periodontitis
Pulpal dx: previously treated
Pre Op #9
Post Op #9
6 Month Re-call #9
1 Year Re-call #9
Case #4
Patient presented for retreatment # 30
(+CBCT scan taken, (+)PAP on both mesial and distal roots, missed DL canal
# 30 (+)perc, (-)palp, previous RCT
#30
Apical: symptomatic AP
Pulpal: previously treated
Retreatment was completed in two visits and was uneventful.
Pre Op #30
Post Op #30
Case #5
Patient presented for RCT # 15
# 15 (-)perc, (-)palp, no response to cold, (+)PAP
#15
Apical: asymptomatic AP
Pulpal: necrotic
RCT was completed and was uneventful.
Pre Op #15
Post Op #15
Case #6
# 19 (-)perc, (-)palp, no response to cold
#19
Apical: symptomatic AP
Pulpal: necrotic
RCT was completed in one visit using bioceramics. Treatment was uneventful.
Pre Op #19
Post Op #19
Case #7
A 12 year old boy presented with dad for eval # 29
# 29 (-)perc, (-)palp, lingering to cold, open apex
#29
Periradicular Dx: normal
Pulpal: irreversible pulpitis
Pre Op #29
Post Op #29
6 Month Re-call #29
Partial pulpotomy was completed, BC putty placed with IRM. Pt referred to his GP for permanent restoration. Pt was reevaluated in 6 month, root appeared more developed and slightly more closed than before, another reeval recommended in 6 months.
Case #8
Patient presented for retreatment of Tooth # 19
Tooth # 19 tested (-)perc, (-)palp, previous RCT CBCT scan taken, (+)PAP distal root, short fill
#19
Pulpal: previously treated
Apical: asymptomatic AP
Pre Op #19
Post Op #19
Case #9
Mr. P presented to our office for evaluation of tooth # 30. His dentist prepped his tooth and placed a temporary crown, pt was having slight sensitivity to cold.
(-)perc, (-)palp, lingering to cold
#30
Pulpal: irreversible pulpitis
Apical: normal
Pre Op #30
Post Op #30
Intresting findings: upon looking at the radiograph we notice very narrow and calcified canals in the mesiobuccal root, these can be very tricky to navigate, we must ensure a good glidepath in order to successfully instrument these canals! The canals are also curved.
Case #10
A 14 year old female presented with parents for root canal treatment # 29. She had her braces removed recently and noticed a large, buccal swelling.
# 29 (+)perc, (+)palp, buccal swelling, no response to cold, (+)periapical lesion
#29
Apical: acute apical abcess
Pulpal: necrotic
Pre Op #29
Working Length Determination
Post Op #29
Treatment was completed in two visits. The goal of the first visit was to get the patient out of pain, I slightly instrumented and irrigated the canal; I placed calcium hydroxide and temporized with cotton pellet and cavit.
On the 2nd visit, she came back two weeks later, her swelling was gone and she was feeling better. We finished the case and the patient was very happy.
Some interesting facts:
The interesting factor was that apex was open and the tooth was necrotic. These are sometimes hard to manage because we don’t want to push our filling materials past the apex. I performed a procedure where I placed 3 mm of BC putty apically and then filled the rest of the canal with bioceramic sealer and Gutta Percha. I was happy that the material was contained and wasn’t pushed outside the apical segment. In order to contain the material, I always take a radiograph with a file and obtain my working length
Case #11
Patient presented for RCT # 14, she states that she had trouble eating and sleeping for a few days.
# 14 (+)perc, (+)biting, no response to cold, (+)periapical lesion
#14
Pulpal: necrotic
Apical: symptomatic AP
Pre Op #14
Post Op #14
Root canal treatment was completed in two visits. On the first visit we cleaned and irrigated all the canals, calcium hydroxide was placed, tooth was temporized with cotton pellet and cavit. On the second visit, patient was asymptomatic, root canal was completed uneventfully.
Intresting findings:
DB canal was very curved and it was difficult to negotiate the curve, I used many instruments to establish a good glidepath and then I was able to instrument the canal uneventfully.